Judging by his most recent scientific production, Doctor of Science José Antonio Guardado Chacón has not wasted time or space in insisting on the potential of using anaerobic biodigesters, not only as a tool for the treatment of waste, but as a renewable energy source (RES). He has just done so, as the organizer of the 3rd Workshop: Biogas, Water and Sanitation Movements or Networks, held within the 2024 Cubasolar International Workshop, held between November 19 and 21 at Quinta de los Molinos.
The scientific event had 160 participants from all Cuban provinces and speakers from Brazil, Guatemala, Spain and Colombia. The poor national media coverage is striking, right in the middle of an energy crisis that forces us to urgently look at the RES, a field in which Cubasolar has worked for 30 years.
The workshop organized by Dr. Guardado Chacón was divided into three panels, which showed successful experiences of the Biogas Users Movement (MUB), both individual and in communities and pork production entities, according to the event’s rapporteur.
But, although there is talk of Movement ― and since 2017 a book published by Cubasolar abounds on the subject ― the use of this RES is not widespread nor does it show the same results in the country. In fact, among the questions that presided over the panels of Cubasolar 2024 was a specific one: How have the MUB and other Renewable Energy Sources in some territories been able to overcome obstacles and become a thriving popular energy model and in other territories, this has not been possible?
Guardado himself had, in part, answered the question in 2021, in an article cited by the IPS news agency. When asked why biogas was among the least developed renewable sources and how this could be reversed, given that Cuba needs to boost national food production, the article responded:
According to the first projections of the RES, to produce electricity given the United Nations 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, biogas is among the least developed (27 MW). This may be due, among other reasons, to the lack of knowledge of what can be contributed from the locality with many small solutions and social inclusion, based on scientific-popular criteria.
In addition, biogas is not precisely for generating electric power, but to stop consuming electricity. Its direct use is much more efficient than if we transform it into electric power. To reverse this position, biogas technology must be assessed integrally, taking advantage of all its final products.
This includes the supply of basic nutrients for the fertilization of soils that directly affect food production. In this regard, work is being done on the organization approved by the highest leadership of the country, which foresees greater participation of the actors of Cuban society, both at the state and non-state levels.
At that time it was estimated that there were about 5,000 biodigesters in Cuba, and the institutional design aimed at each municipality having “a development program and strategy regarding biogas, whose management and implementation must be articulated with the plans of the province.”
For this note, we found no evidence that these strategies exist in all the Cuban municipalities, as indicated by Ministerial Order 395 of April 2021, of the Ministry of Energy and Mines. They must not be very complete when the Cubasolar 2024 Rapporteur lists as one of the key questions of the event: What hinders the development of local energy self-sufficiency in the municipality? Why are other urgent issues put before energy in the strategies?
Maximizing the contributions of biogas, on paper
The truth is that of the best-known RES, biogas is the only one that, in addition to its energy potential, has a very high component of environmental sustainability, by using polluting waste from the agricultural and agri-food sectors.
Scientific production on this topic is abundant. From the one that explores the introduction of technologies and their economic and environmental feasibility (Biogás y sostenibilidad en Cuba) — “in the 1970s, around 550 small biogas installations were built, with traditional Chinese and Indian technologies, in dairy farms and pig farms” — through to recommendations for the construction of biodigesters (Diseño y construcción de plantas de biogás sencillas) — published in 2007 — to the assessment of the potentials and the preparation of a Atlas de Bioenergía. Cuba Edición 2022.
Reading this latest article, with its detailed analysis of the calculation of the biogas production potential — from excrement associated with the raising of pigs, poultry, and cattle — it is difficult to assimilate that this RES has not advanced further along the path that, right now, is proposed as mandatory by Decree Law 110/2024 of the Council of Ministers, whose First Transitional Provision establishes that “high consumers existing at the time of publication of this Decree in the Official Gazette of the Republic of Cuba, have a period of up to three years to install renewable energy sources, to generate at least fifty percent of the electricity they consume during peak daytime hours.”
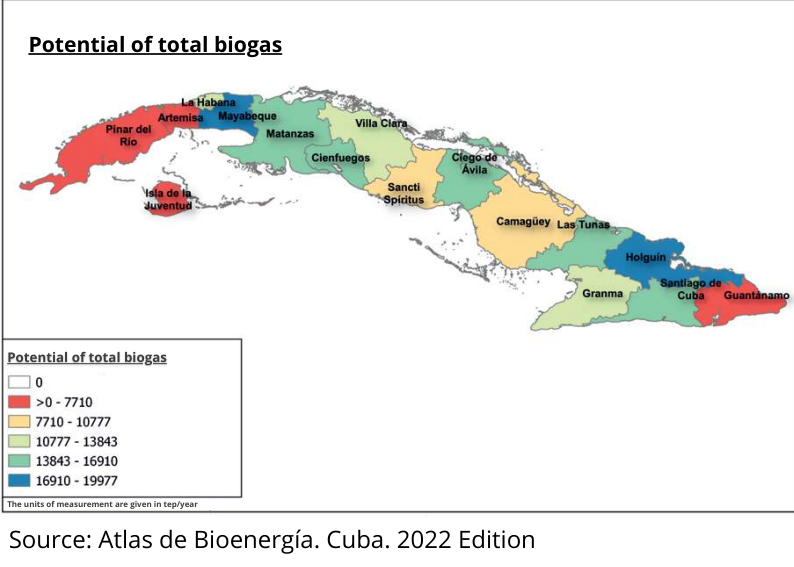
According to Atlas, “the total biogas production potential, which includes the associated agricultural and industrial production, amounts to 615,595 m3/year, which is equivalent to 189,227 tep/year or 710,095 MWh/year. 63% of the total corresponds to agricultural production.”
Of this potential, more than half is concentrated in six provinces: Matanzas, Holguín, Mayabeque, Santiago de Cuba, Ciego de Ávila, and Cienfuegos, as shown in the map prepared by the group of authors.
The chapter dedicated to biogas concludes by stating that, “taking into account the potential for biogas production and the structure of electricity and fuel consumption, it has been found more reasonable to consider that biogas be used for electricity production rather than for replacing fuels in furnaces and boilers.”
Likewise, the analysis of the potential impact that can be achieved by using biogas for power generation, confirmed the researchers, “allows us to see that 44% of the electricity consumed by the three sectors included in this report can be generated. The power generation potential in AZCUBA is 34% of its total consumption; in the agricultural and forestry sector it is 117% and in the food industry 6.5%.”
In other words, three sectors that consume a lot of electricity in Cuba have the energy potential to be self-sufficient in their own backyards — or at least to reduce their dependence on the National Electric Power System — and, nevertheless, the experiences of its application can be counted on one hand.
All this even though the Policy for the prospective development of renewable sources and the efficient use of Energy 2014-2030, approved a decade ago, proposes in its Strategic Objective (SO) 6: “maximize the use of renewable energy sources with a circular economy approach to contribute to food security, sustainability and sovereignty and the reduction of the environmental footprint of the agro-industrial and food production sector”; and in SO 7: “maximize the energy contributions of the agro-industrial and forestry sector.”
Even so, the practical and validated examples of the use of biogas are concentrated, fundamentally, in the microlocal scenario.
This is the case of the El Colorado Porcine Base Business Unit (UEBP) and the surrounding rural community, located in the Cabaiguán municipality, in the province of Sancti Spíritus, where the GEF-UNDP Biomas-Cuba project (of the Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation) made it possible to build two fixed dome biodigesters (modified Chinese model) in 2020, with 45 m3 and 50 m3 of digestion, respectively. Both biodigesters treat the excrement of 600 pigs (50% of the animal mass of the UEBP).
The 90 m3 of biogas produced daily not only supplied the porcine entity but also reached more than 30 homes through a high-density polyethylene network that distributed the biofuel. Electricity consumption automatically decreased by between 30 and 60%, equivalent to 18.3 MWh/year.
From an environmental point of view, “the daily consumption of 90 m3 of biogas for cooking made it possible to avoid felling 24 ha/year, avoided the emission of 59.8 t of CO2eq/year, or 1,255 tons of methane, and produced 4 t/year of effluents, which is used as biofertilizers for soil improvement.”
An example of biodigesters on another scale is being developed in the Martí municipality, in Matanzas. In April 2023, the IPS agency elaborated on the scope of the local development project with international cooperation (European Union and UNDP) that would put public buses into circulation with biomethane as fuel, while producing electricity and biofertilizers for organic crops, with direct benefit for the 22,000 inhabitants of the municipality and surrounding areas.
Although the local press has recently referred to the project, the progress of the investment is not specified, which is expected to be completed this year according to the initial design.
But, just as one swallow does not make a summer, isolated good practices in the use of anaerobic biodigestion of waste do not allow for the qualitative and quantitative leap with this technology. Hence, in July 2021, Doctor of Science Roberto Sosa Cáceres, deputy director of the Center for Information Management and Energy Development (Cubaenergía), stated in the Renovable.cu bulletin that Cuba has untapped biogas potential, both in the state sector and in the cooperative and individual farmer sector.
In Sosa’s opinion, the country does not have the necessary technologies to build industrial biogas plants and it is necessary to create “a technological culture of efficient use of this resource, high knowledge and production of specialized equipment.”
A decade ago, the same expert, then director of the Center for Promotion and Development of Biogas at the Porcine Research Institute, was more optimistic. In an interview with Granma, he spoke of a national program to manufacture a thousand biodigesters annually until 2020. There would be, at least, 6,000 new sites to date, but ― as we pointed out at the beginning ― in 2021, less than 5,000 were estimated.
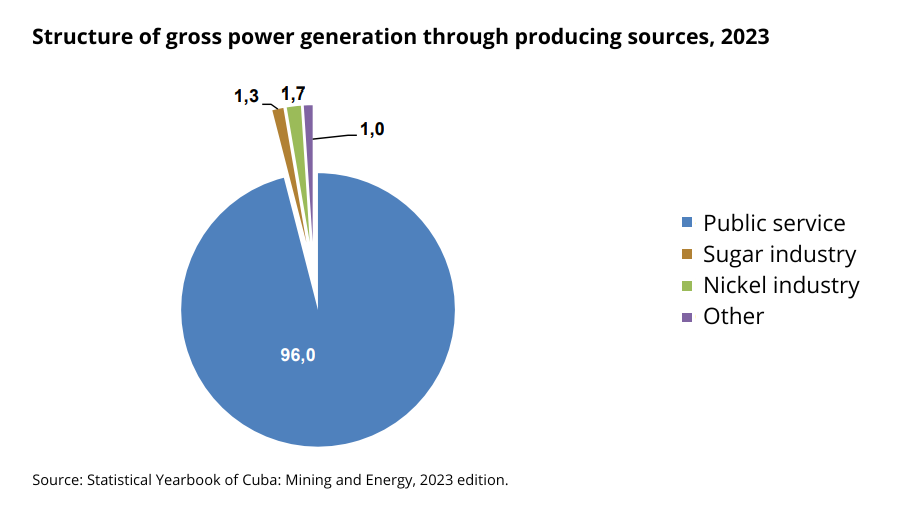
Although there has been a gradual increase in gross power generation from waste since 2019 (from 2.5 Gigawatt/hour to 159 in 2023), biogas plants (plus emerging groups, according to the nomenclature of the Statistical Yearbook. Cuba. Mining and Energy. 2023 Edition), barely produce 1.03% of the total electricity in Cuba.
 The current levels of pork and beef production in the country, with a sustained decrease in mass, also constitute a major obstacle to the generation of energy through anaerobic biodigesters, as the waste from these activities is the main source of energy. However, any organic waste can be converted into fuel.
The current levels of pork and beef production in the country, with a sustained decrease in mass, also constitute a major obstacle to the generation of energy through anaerobic biodigesters, as the waste from these activities is the main source of energy. However, any organic waste can be converted into fuel.
That is why experts continue to firmly believe that “anaerobic technologies have a promising future in their implementation in the agricultural and industrial framework of Cuba, by promoting the development of the circular economy, promoting the recovery of resources.” This is what researchers Deny Oliva and Ileana Pereda say in a scientific article on the subject. They conclude:
It is worth emphasizing that in order to increase the application of this type of technology, a significant effort is needed from the scientific, specialized, and business community and decision-makers in the country to appropriate them and to “tropicalize” the technological solutions, in addition to adapting the national industry to assume part of the components necessary for its expansion. It is essential to increase scientific research and innovation in-house that allows the implementation to be adjusted to the specific conditions of the country.